The Hidden Saboteur in Your Cells: How Deuterium Impacts Your Health—and What to Do About It
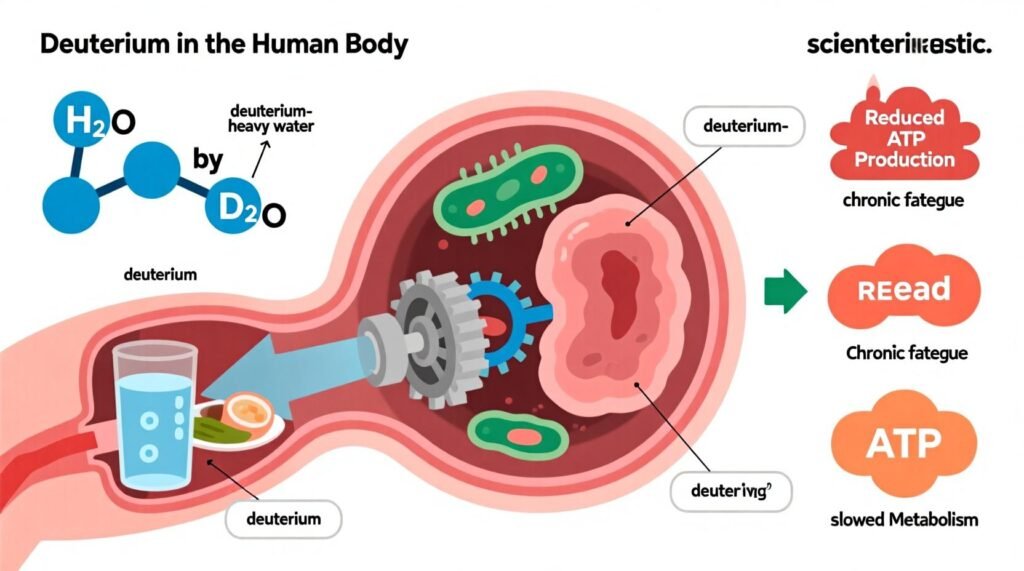
Picture your body like a high-performance sports car. Your mitochondria are the engines; hydrogen protons are the fuel that spins the micro-turbines to make ATP, your energy currency. Now imagine a few heavy pebbles slipping into the engine—everything still runs, but it runs slower and wears out faster. Those “pebbles” are deuterium, a heavy form of hydrogen that, in excess, can bog down your cellular engines. You’ll learn what deuterium is, why it matters for energy, metabolism, skin, and brain health, and exactly how to lower your burden—safely and practically—over the next 90 days.
What Deuterium Is (and Why Its “Weight” Matters)
Deuterium (²H or D) is a naturally occurring isotope of hydrogen. Unlike ordinary hydrogen (one proton), deuterium carries an extra neutron, making it twice as heavy. It’s found everywhere—in water, food, and your tissues. Seawater averages ~150 parts per million (ppm) of deuterium; that doesn’t sound like much, but at the nanoscopic scale of enzymes and membranes, mass matters.
Your mitochondria make ATP by spinning a rotor (ATP synthase) with a stream of ultra-light protons. When heavier deuterium sneaks into that stream, it moves differently and can “jam” the rotor, reducing output and increasing wear. Think: swapping a race-tire for a tractor wheel—everything turns, just less efficiently.
How Excess Deuterium Can Show Up in Your Life
When the rotor slows, downstream effects stack up:
- Lower ATP production → energy slumps you can’t caffeine your way out of
- Higher oxidative stress → faster “rusting” of tissues (skin, joints, brain)
- Slower cellular repair → reduced resilience after workouts or illness
- Altered signaling → hormonal wobble, sleep/mood issues, and brain fog
Higher deuterium loads are associated with metabolic slowdown, fatigue, accelerated aging, and risk elevations for conditions like insulin resistance and neurodegenerative disease. Some tumor cells may even thrive in high-deuterium environments. These ideas remain under active study, but the mechanisms are biologically plausible given isotope effects.
Deuterium is like fine sand in your cellular gears—tolerable in tiny amounts; in excess, friction rises and everything feels harder.
Where Deuterium Hides: Food & Water
Deuterium level varies by climate, water source, and metabolism of the organism you’re eating.
Typically higher (~150–160+ ppm):
- Tropical fruits (banana, mango, pineapple), fruit juices
- Grains (wheat, rice, oats, corn) and starchy tubers (potato, sweet potato)
- Processed foods/drinks (often made with high-D tap water), beer, sugary alcohols
- Some tropical plant oils (palm, coconut)
Moderate (~140–150 ppm):
- Temperate fruits (apples, pears, berries)
- Leafy greens, carrots
- Dairy (varies by origin and feed)
Lower (~125 ppm or less):
- Grass-fed meats and fats from colder climates; deep ocean fish
- Avocados, olives/olive oil; pasture-raised eggs (cold climates)
Choosing seasonal, local produce and grass-fed, cold-climate animal products naturally lowers your deuterium intake without fuss.
Strategies to Lower Your Deuterium Burden
Hydration: Consider Low-Deuterium Water (LDW)
Use naturally low-D glacial sources or specialty fractionated/distilled products; even 30–50% replacement shifts your overall intake. Brands exist (e.g., Preventa®, Qlarivia®), but any reduction via dilution helps.
Food Pattern: Swap in Low-D Staples
Build meals around wild fish, grass-fed meats, eggs, olive oil, avocado, and temperate vegetables. Ease back on tropical fruits, grains, juices, and ultra-processed foods.
Metabolic Levers: Make More Low-D “Metabolic Water”
- Low-carb/keto cycles shift fuel from glucose (higher D) to fats (lower D).
- Intermittent fasting (16:8) supports mitochondrial repair and turnover.
- Exercise (cardio + resistance) increases mitochondrial density.
- Cold exposure (showers, winter walks) activates brown fat, which generates low-D water.
Mitochondrial Support: Protect the “Rotor”
- Morning light exposure (10–15 min) to align circadian energy signaling.
- Polyphenols (green tea, rosemary, turmeric) to buffer oxidative stress.
- Minerals/cofactors: magnesium glycinate 300–400 mg/day; CoQ10 100–200 mg/day. Always check with your clinician.
Reality Check: You Can’t “Cook Out” Deuterium
Kitchen methods won’t strip D from food. Fermentation, sprouting, or sun-drying may modestly alter fractions—but diet pattern and metabolism matter far more.
90-Day Deuterium Reset
Phase 1 (Days 1–30): Foundation
- Replace 30–50% of daily water with LDW.
- Swap high-D staples for low-D proteins/fats and temperate vegetables.
- Morning sunlight (10–15 min); consistent sleep/wake; CoQ10 100 mg + Mg glycinate 300–400 mg daily.
Phase 2 (Days 31–60): Metabolic Switch
- Keep LDW at ≥50% of intake.
- Start 16:8 intermittent fasting; reduce carbs to <50 g/day (short low-carb/keto cycle).
- Training: 2×/week strength + 2–3×/week aerobic.
- Add cold exposure 3–4×/week. Optional: NMN 250–500 mg or niacinamide 250 mg, PQQ 10–20 mg.
Phase 3 (Days 61–90): Deep Depletion & Resilience
- Maintain LDW 50–70%; 2 meals/day; introduce 18:6 fasting or 24-hr fast once/month.
- Cardio: Zone 2 (2×/week) + HIIT (1–2×/week); continue 2×/week strength.
- Recovery: red/near-infrared light 10–15 min, 3–5×/week; cool, dark bedroom; consistent schedule.
Sarah, 42, swapped her morning orange juice for LDW, added 16:8 fasting, and prioritized sunlight. Within weeks, her energy lifted and the scale nudged in the right direction—without changing her workouts.
Myth vs. Reality
- Myth: Deuterium is universally bad.
Reality: Your biology evolved with some deuterium; the goal isn’t zero—it’s avoiding excess while supporting mitochondrial efficiency. - Myth: There’s a magic product that removes deuterium from foods.
Reality: No home method reliably strips deuterium; pattern and metabolism matter more. - Myth: Results are instant.
Reality: Mitochondrial shifts are gradual. Think 90-day horizons for measurable changes in energy, recovery, and body composition.
How to Track Progress
- Energy consistency and fewer mid-afternoon crashes
- Workout recovery and soreness window
- Sleep quality (subjective score; smart-ring metrics if used)
- Body composition (waist-to-hip, progress photos)
- Metabolic markers (home fasting glucose trends, if tracked)
Quick-Glance Lists
Low-Deuterium Pantry Starters
- Proteins: wild salmon/sardines, grass-fed beef/lamb, pasture-raised eggs
- Fats: extra-virgin olive oil, avocado, grass-fed butter/ghee
- Carbs: leafy greens, zucchini, crucifers; berries in moderation
Rotate Down (Not Ban Forever)
- Tropical fruits and juices; grains and starchy tubers
- Ultra-processed snacks; beer and sugary alcohols; corn-syrup-sweetened drinks
Start Your Deuterium Reset Today
Replace 30% of your daily water with LDW and swap one high-D item (fruit juice, grain-heavy dinner) for a low-D option (herbal tea, extra veggies + olive oil). For a done-for-you plan with meal templates, shopping lists, and weekly workouts, download the free 90-Day Deuterium Reset Guide and follow the phase plan—one simple change at a time.
By Ian Kain, Natoorales.com
Discover transformative holistic wellness programs and trauma release therapy online. Remote healing for clients seeking natural solutions natoorales.com |
ps